What Is Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)?
Sickle cell anemia, also known as sickle cell disease (SCD), is a red blood cell disorder caused by a genetic mutation (RBCs). RBCs are normally formed like discs, which allows them to pass through even the smallest blood channels.
The RBCs in this condition, on the other hand, have an aberrant crescent form that resembles a sickle. This makes them sticky and inflexible, and they’re more likely to get stuck in small veins, preventing blood from reaching various sections of the body.
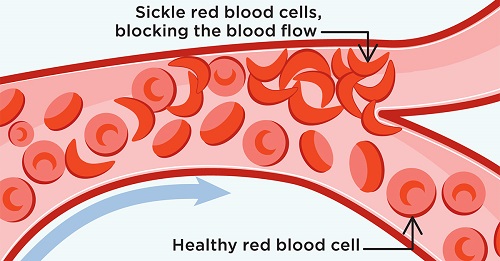
This might result in tissue damage and pain. This can result in pain as well as more serious complications such as infection, acute chest syndrome, and stroke. A simple blood test is used to detect SCD. It’s most commonly discovered at the hospital during normal newborn screening exams.
SCD can also be detected prior to delivery. People who live in areas where malaria is endemic are more likely to be carriers. This covers people from Africa, India, the Mediterranean, Saudi Arabia from around the world.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of sickle cell anemia commonly begin around the age of five months. They differ from one individual to the next and evolve with time. The following are examples of signs and symptoms:
- Anemia: Sickle cells readily disintegrate and die, leaving you with an insufficient number of red blood cells. Red blood cells last approximately 120 days before needing to be replaced. However, sickle cells normally die in 10 to 20 days, leaving a red blood cell shortage (anemia).
- Painful episodes: Pain crises, or periodic episodes of pain, are a common symptom of sickle cell anemia. Pain occurs when sickle-shaped red blood cells impede blood flow to your chest, abdomen, and joints through tiny blood channels. Bone pain is also a possibility. The discomfort can range in intensity and linger anywhere from a few hours to several weeks. Some folks only have a couple of pain crises every year. Others suffer from a dozen or more pain crises every year. A hospital stay is required in the event of a serious pain crisis.
Hackensack Meridian Health - Hands and feet swell up: Sickle-shaped red blood cells limit blood flow to the hands and feet, causing edema.
- Late Puberty or delayed growth: Red blood cells transport oxygen and nutrients throughout your body, allowing you to thrive. In newborns and children, a lack of healthy red blood cells can limit growth and cause puberty to be delayed.
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital - Issues with the vision: Sickle cells can clog the tiny blood arteries that supply your eyes. This can cause vision issues by damaging the retina, which is the part of the eye that interprets visual images.
Treatment And Cure:
People with SCD begin to show symptoms within their first year of life, usually around the age of five months. SCD symptoms and implications vary from person to person and can be moderate to severe.
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for everyone with SCD. Depending on the symptoms, each person’s treatment options vary. SCD can only be cured through bone marrow or stem cell transplant.
Bone marrow is a soft, fatty substance located within the middle of the bones that produces blood cells. A bone marrow or stem cell transplant is a treatment that involves taking healthy blood-forming cells from one person (the donor) and transplanting them into someone whose bone marrow is malfunctioning.
Transplants of bone marrow or stem cells are extremely dangerous and can result in death. The bone marrow must be a close match for the transplant to function. A brother or sister is usually the ideal donor.
Bone marrow or stem cell transplants are reserved for children with severe SCD who have minimal organ damage as a result of the condition.
Also Read: Covid 19 Infection Impairs Functioning Of Brain’s Grey Cells