Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive and degenerative brain disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite extensive research and efforts to find a cure, there is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. However, recent breakthroughs in drug development have shown promise in slowing the progression of the disease and reducing its effects on the brain.
The first drug that has been shown to actively destroy the brain in Alzheimer’s disease is a new class of drugs called anti-amyloid drugs. These drugs target a protein called amyloid-beta, which accumulates in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients and is thought to play a key role in the progression of the disease.
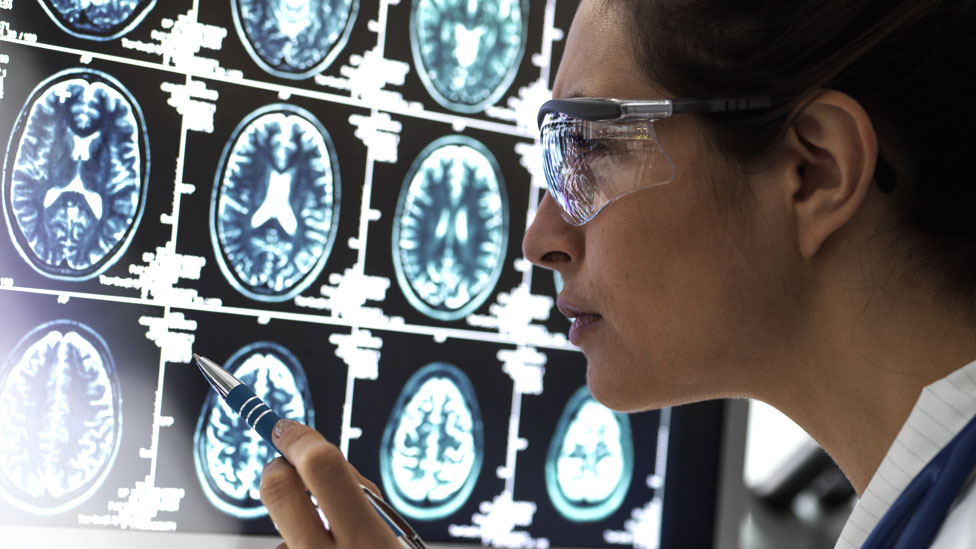
The Discovery
The discovery of anti-amyloid drugs marks a momentous milestone in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease. For the first time, researchers have found a drug that can actively target and destroy the toxic protein that is responsible for the progression of the disease.
One of the most promising anti-amyloid drugs is aducanumab. Aducanumab has been shown to significantly reduce amyloid-beta levels in the brain and slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease in clinical trials. These results are exciting and offer hope for those affected by Alzheimer’s and their families.
However, it is important to note that while anti-amyloid drugs offer promise, they are not a cure for Alzheimer’s disease. Further research is needed to determine the long-term effectiveness of these drugs and to fully understand their mechanisms of action.
Other treatments and therapies
In addition to anti-amyloid drugs, some other treatments and therapies can help to manage the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. These include cognitive and behavioural therapies, as well as medications to manage agitation, depression, and other behavioural symptoms. To fully understand the potential of anti-amyloid drugs, it is important to continue funding research and development in this field. The discovery of anti-amyloid drugs marks a significant step forward in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease, but more work is needed to turn this promise into a reality.
Staying mentally active
In addition to anti-amyloid drugs, there are also other strategies that individuals can adopt to reduce their risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. One of the most important is maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep.
Staying mentally active by engaging in activities such as reading, doing crossword puzzles, or playing brain games can also help to reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Social engagement and staying connected with friends and family are also important for maintaining cognitive health.
Reducing stress levels and managing chronic medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, can also play a role in reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can also help to reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
It is important to remember that while these strategies may help to reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, they are not a guarantee against developing the disease. It is also important to consult with a doctor or healthcare professional before starting any new lifestyle changes.
Personal prevention efforts
In addition to research and personal prevention efforts, it is also crucial for society to work towards creating a supportive environment for those affected by Alzheimer’s disease. This includes providing adequate care and resources for individuals with Alzheimer’s and their families, as well as increasing public awareness and understanding of the disease.
Caregivers of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease face significant physical, emotional, and financial burdens. Society needs to provide them with the support and resources they need to effectively care for their loved ones. This may include access to respite care, support groups, and financial assistance.
Increasing public awareness and understanding of Alzheimer’s disease can also help to reduce the stigma associated with the disease and improve the quality of life for those affected by it. This can include educating the public about the signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, as well as promoting a better understanding of the challenges faced by individuals with Alzheimer’s and their families.
Finally, society needs to continue funding research into Alzheimer’s disease, to find a cure and improve treatments for those affected by the disease. The discovery of anti-amyloid drugs is a promising step forward, but more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and determine their long-term effectiveness.
Conclusion
The discovery of anti-amyloid drugs that actively destroy the brain in Alzheimer’s disease is a momentous milestone in the fight against this devastating disease.
In addition to personal prevention efforts and continued research, it is also important for society to work towards creating a supportive environment for those affected by Alzheimer’s disease, providing adequate care and resources, reducing stigma, and increasing public awareness. By working together, we can bring one step closer to finding a cure for Alzheimer’s disease.
While more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of these drugs, individuals can also take steps to reduce their risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease by adopting a healthy lifestyle and reducing stress levels. By working together, we can bring one step closer to finding a cure for Alzheimer’s disease.
These drugs offer hope for those affected by Alzheimer’s and their families, but more research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and determine their long-term effectiveness. By supporting continued research and development, we can bring one step closer to a cure for Alzheimer’s disease.
























