Monoclonal antibodies are being evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other regulatory agencies across the world for use as a treatment for COVID-19.
Monoclonal antibodies are proteins created in a lab that replicate the immune system’s ability to attack dangerous antigens like viruses (They are immunoglobulins that are identical and are produced from a single B-cell clone).
Sotrovimab is a monoclonal antibody that is directed against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 and is used to prevent the virus from attaching to human cells and infecting them. Monoclonal antibodies are distinguished from polyclonal antibodies by their origin in a single B-cell clone and subsequent targeting of a single epitope.

It is feasible to make monoclonal antibodies that precisely bind to practically any chemical and may subsequently be used to detect or purify that substance. In biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine, this has become a valuable tool.
“We are offering another alternative to assist keep high-risk COVID-19 patients out of the hospital with the approval of this monoclonal antibody treatment,” said Patrizia Cavazzoni, M.D., head of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “It’s critical to broaden the arsenal of monoclonal antibody therapies that are predicted to preserve effectiveness against circulating variants,”.
The FDA determined that it is reasonable to believe that sotrovimab may be beneficial in treating adults and some pediatric patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 after reviewing all available scientific evidence. Furthermore, when used to treat COVID-19 in the authorized population, the drug’s known and potential benefits outweigh the drug’s known and potential hazards.
The majority of people who recover from COVID-19 produce antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 virus in their bodies. These antibodies are reported to last for at least 5–7 months following infection, according to scientists.
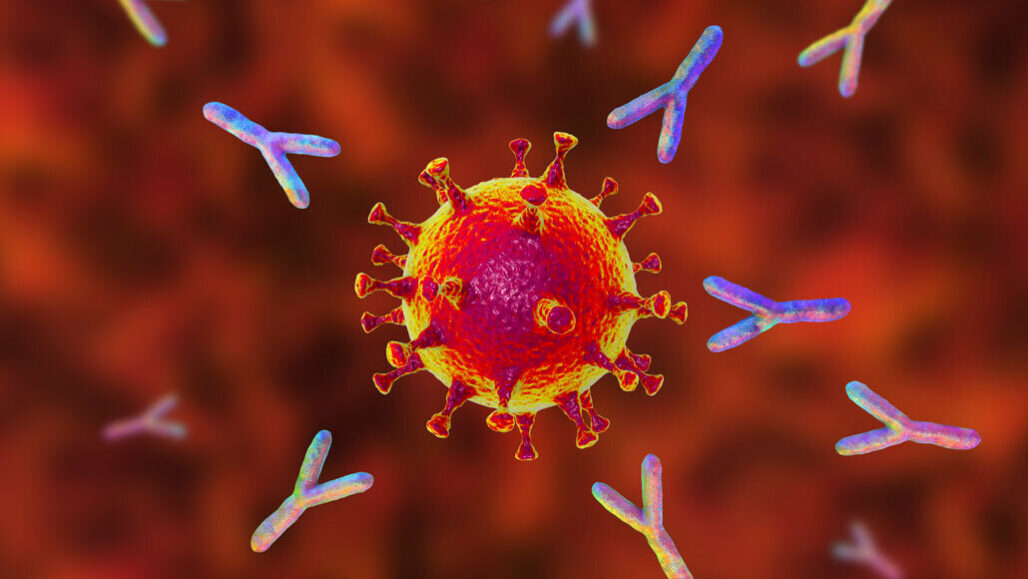
Scientists can, however, make these antibodies in the lab and inject them into the bloodstream. Each monoclonal antibody recognizes only one antigen. There are numerous approved monoclonal antibody treatments for COVID-19.
The spike glycoprotein on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 virus facilitates the virus’s entrance into the body’s cells. Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 attach to the spike protein, preventing the virus from entering the cell. Currently, all monoclonal antibodies for COVID-19 that have received emergency use authorization from the FDA are directed towards the spike protein.

However, Getting immunized and continuing to follow non-pharmaceutical measures like mask-wearing and physical separation are the most effective ways to avoid COVID-19. More therapy options are gradually becoming accessible for patients who develop COVID-19.
Within a few days of receiving a COVID-19 diagnosis, monoclonal antibody therapies are most successful. If a person has COVID-19 symptoms and is in a high-risk category, they should consult with a healthcare expert about the treatment choices available and whether one is right for them.
Also Read: Home Remedies And Organic Measures For An Immunity Boost





















